Frequently Asked Questions (Work in Progress)
What causes Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)?
Tuberous sclerosis complex is a genetic disease. A change (mutation/pathogenic varient) in the TSC1 or TSC2 gene, which normally suppress cell growth, lead to abnormal tissue and tumor growth causing Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC). Only one of the genes needs to be affected for TSC to be present. The TSC1 gene is located on chromosome 9 and is called the hamartin gene. The other gene, TSC2, is located on chromosome 16 and is called the tuberin gene. TSC is autosomal dominant which means it is not linked to the sex genes and males and females have an equal risk of having the condition.
It can be inherited from one parent with TSC or can result from a spontaneous genetic mutation. About one-third of people with TSC inherited the genetic condition from a parent. However, for the other two-thirds, the condition is "spontaneous," meaning that the change is the first time of that change in the child's family. A parent with tuberous sclerosis has a 50 percent chance of passing the condition to their children.
Sometimes it is found that a child with TSC has a parent who also has the condition but didn’t know it. If your child is diagnosed with TSC, you may want to check that you dont also have it.
If you have one child with TSC, there is an increased chance that your other children will also have the condition.
More informatio about the genetics of TSC https://www.tscalliance.org/understanding-tsc/genetics/
More information on autosomal dominant inheritance https://www.genomicseducation.hee.nhs.uk/genotes/knowledge-hub/autosomal-dominant-inheritance/
How common is TSC?
TSC affects approximately 1: 6,000 to 1: 10,000 live births. It is estimated there are between 1-2 million people in the world living with TSC. Many cases may remain undiagnosed for years or decades due to the relative obscurity of the disease and the mild form symptoms may take in some people.
What is the treatment and is there a cure?
There is no cure, but symptoms are managed with medications (like mTOR inhibitors for tumors), therapies (physical, occupational, speech), and sometimes surgery for tumors or severe epilepsy. There are international clinical consensus guidelines for the dignosis, surveillance and management of the symptoms. (See section on Diagnosis & Management)
What is the prognosis?
TSC varies widely from affecting people mildly to very severely and symptoms change over time; many live full lives with a normal lifespan, though some can face severe challenges. There can be complications in some organs such as the kidneys and brain that can lead to severe difficulties and even death. To reduce these dangers, people with TSC should be monitored throughout their life by their physician for potential complications. Thanks to research findings and improved medical therapies, people with tuberous sclerosis complex are experiencing better health care than before. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/tuberous-sclerosis-complex
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex symptom emergence and progression Adapted from Northrup et al., 2021
Are the tumours cancerous?
No. The tumors resulting from TSC are not cancerous and not as severely unregulated as in cancer, but these tumors may still cause serious problems. The tumours in the brain can cause epilepsy and seizures, as well as TSC- Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders (TAND) which include behavioural, intellectual, academic, psycological, psychiatric and neuropsychological difficulties. They can also cause disruption to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CS F) making a child seriously ill. The tumors in the kidney (renal angiomyolipomas) can become so large they eventually disrupt normal kidney function or bleed which can be life threatening. Heart tumors, called cardiac rhabdomyomas, can cause problems if they are blocking the flow of blood or cause abnormal heart rythms (arrhythmia). Lung tumours lymphangioleimyomatosis (LAM) primarily affecting women, lead to lung destruction and breathing issues.
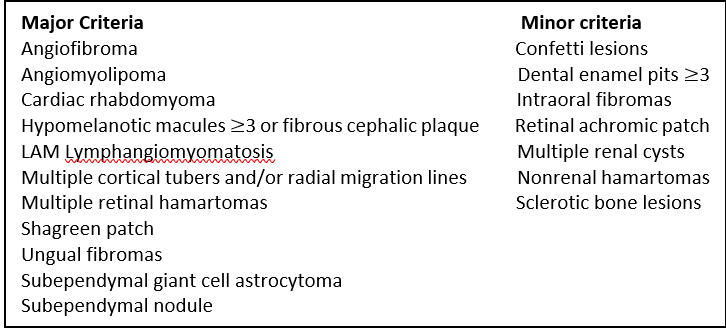
What are the Diagnostic Criteria and Surveillance Recommendations ?
In 2012, the International Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Consensus Conference reviewed prevalence and specificity of TSC-associated clinical manifestations and updated the TSC diagnostic criteria from 1998. Clinical features of TSC continue to be a principal means of diagnosis but include additional clarification and simplification. In addition, TSC may now be diagnosed via genetic testing. The new clinical and genetic diagnostic criteria of 2012 are summarized below
Diagnostic Criteria
Definite TSC: Two major features or one major feature with 2 minor features. Possible TSC: Either one major feature or > 2 minor features. **A combination of the two major clinical features LAM and angiomyolipomas without other features does not meet criteria for a Definite Diagnosis.
Surveillance Recommendations
Individuals with a diagnosis of TSC require lifelong surveillance. At the time of diagnosis, many medical tests are performed and international consensus recommendations determine ongoing monitoring surveillance protocols. The following tables show surveillance screening for TSC according to the International Consensus recommendations Click here.
-
There are links to the diagnostic criteria on top of our Diagnosis page. They can also be accessed from here; general TSC diagnostic criteria and a TAND checklist with clinical consensus guidelines.
Medication Information
There are several types of medication used in the treatment of Tuberous Sclerosis and new medications are continuously being discovered and used. It is important to stay updated and obtain accurate information form reliable sources.
Medicines.ie, is Ireland’s central, regulator approved online resource of accurate information on medicines available in the Republic of Ireland. It provides information for healthcare professionals and the public through Summary of Product Characteristics (SPCs), Patient Information Leaflets (PILs) and Educational Materials. It is owned by the Irish Pharmaceutical Healhcare Association (IPHA) and designed for easy searching and accessing crutiol drug details https://www.medicines.ie/
Where can I find more information about TSC?
There are excellent websites hosted by TSC organisations worldwide where you will find extensive and comprehenssive information resources and direction. We highly recommend you consult them.
TSCAlliance https://www.tscalliance.org/
Tuberous Sclerosis Association UK (TSA UK) https://tuberous-sclerosis.org/
Tuberous Sclerosis Australia https://tsa.org.au/
Tuberous Sclerosis International (TSCi) https://www.tscinternational.org/
Glossary
General Terms and Genetics
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC): A genetic, multisystem, autosomal dominant disorder caused by mutations in the TSC1 or TSC2 genes, leading to benign tumor growth throughout the body.
TSC1: The gene on chromosome 9 that produces the protein hamartin.
TSC2: The gene on chromosome 16 that produces the protein tuberin.
Hamartin/Tuberin Complex: Proteins that act as tumor suppressors by regulating the mTOR pathway.
mTOR (Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin): A pathway that regulates cell growth and proliferation; when hyperactivated due to TSC1/2 mutations, it leads to tumor formation.
mTOR Inhibitors (Rapalogs): Medications (e.g., everolimus, sirolimus) that block the overactive mTOR pathway to shrink tumors.
Autosomal Dominant: A genetic pattern where a child has a 50% chance of inheriting the disease if one parent has it.
Sporadic/De Novo Mutation: A new genetic mutation that occurs in a child without either parent having the disease; occurs in 2/3 of cases.
Variable Expressivity: A feature of TSC where symptoms vary widely in severity, even within the same family.
Hamartoma: A benign, noncancerous tumor composed of an overgrowth of cells and tissues that are normally present in that organ.
Phakomatosis: A term used to describe systemic disorders (like TSC) characterized by lesions in the skin, eyes, and central nervous system.
TAND (TSC-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders): A term for the wide range of cognitive, behavioral, and psychiatric manifestations of TSC, affecting 90% of individuals.
Brain (Neurological)
Cortical Tuber: A disorganized area of brain tissue (hardened swelling) that is typically found in the cerebral cortex and is associated with epilepsy and developmental issues.
Subependymal Nodule (SEN): Small, often calcified, lesions that protrude from the walls of the cerebral ventricles.
Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma (SEGA): A benign, slow-growing tumor that develops from a SEN and can obstruct cerebrospinal fluid flow, potentially causing hydrocephalus.
Epileptic Spasms (Infantile Spasms): A specific type of seizure common in young children with TSC, often treated with vigabatrin.
Medically Refractory Epilepsy: Seizures that do not respond well to anti-seizure medications.
Hydrocephalus: A dangerous build-up of fluid in the brain, often caused by a SEGA blocking the ventricles.
Skin (Dermatological)
Hypomelanotic Macules ("Ash Leaf Spots"): Lighter-than-normal skin patches often present at birth, a very common early indicator of TSC.
Facial Angiofibromas: A reddish, often butterfly-shaped rash of blood vessels and fibrous tissue on the nose and cheeks.
Shagreen Patch: A patch of thick, leathery, dimpled skin, typically found on the lower back or neck.
Ungual Fibroma (Koenen’s Tumor): Small, fleshy tumors that grow around or under the nails.
Fibrous Cephalic Plaque: A raised, fibrous, often brown lesion found on the forehead or scalp.
Confetti Skin Lesions: Tiny (1-2 mm) white spots often found on the extremities.
Wood’s Lamp: A UV light used to visualize hypomelanotic macules, especially in fair-skinned individuals.
Kidney (Renal)
Renal Angiomyolipoma (AML): A very common (75-80%) benign, but vascular, tumor of the kidney that can cause serious bleeding (hemorrhage) if it grows larger than 3-4 cm.
Renal Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys, sometimes indicating a deletion in the TSC2 and PKD1 genes.
Embolization: A procedure to block blood flow to a kidney tumor, used to stop bleeding.
Lungs
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM): An, almost exclusively female, disease where abnormal muscle cells grow in the lungs, creating cysts, reducing lung function, and causing pneumothorax.
Pneumothorax: A collapsed lung caused by air leaking into the space between the lung and chest wall, often caused by LAM.
Heart (Cardiac)
Cardiac Rhabdomyoma: Benign tumors in the heart, common in infants with TSC and typically regress spontaneously with age.
Eyes
Retinal Hamartoma (Phakoma): A benign, often greyish-yellow, growth on the retina.
Other Terms
Dental Enamel Pits: Small, shallow, or deep pits in the teeth enamel, found in most adults with TSC.
Surveillance: The lifelong, regular monitoring of organs (via MRI, CT, EEG, etc.) to catch complications early.
More in depth glossary
ADHD :Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is a medical/neurobiological condition in which the brain’s neurotransmitter chemicals; noradrenalin and dopamine do not work properly. ADHD is highly prevalent in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC), affecting 30–50% of individuals, which is 10 times higher than the general population. As part of TAND (TSC-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders ) it often manifests with inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, frequently appearing alongside epilepsy or intellectual disability. Management requires tailored educational plans and careful pharmacological treatment, as ADHD meds can interact with epilepsy treatment
https://tandconsortium.org/about/#tand
https://adhdireland.ie/general-information/what-is-adhd/
AML: Angiomyolipoma are benign, highly vascular, fat-rich tumors that occur in 70%–80% of Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) patients, caused by mTOR pathway overactivation. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6399480/
ASD: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is highly prevalent in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC), affecting up to 69% of individuals. It is a major component of TSC-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders (TAND). Early identification is crucial. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8639652/
Autosomal: means traits or conditions are linked to non-sex chromosomes, affecting all genders equally, unlike sex linked traits https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Autosomal-Dominant-Disorder
https://www.genomicseducation.hee.nhs.uk/genotes/knowledge-hub/autosomal-dominant-inheritance/
Cardiac Rhabdomyoma: Cardiac rhabdomyomas are the most common benign, often multiple, heart tumors in children with Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC), typically appearing in fetal or neonatal stages and frequently disappearing by age 3. While usually asymptomatic, large tumors can cause obstruction, arrhythmias, or heart failure. Monitoring is standard, with mTOR inhibitors (e.g., sirolimus) now used for symptomatic cases. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560609/#:~:text=Cardiac%20rhabdomyoma%20is%20a%20rare,in%20descending%20order%20of%20prevalence.
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is the molecule carrying genetic instructions for life, forming a double helix structure like a twisted ladder. The sequence of these bases encodes genes, which direct the building and functioning of all organisms, determining traits and passing hereditary information from parents to offspring. https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Deoxyribonucleic-Acid-DNA#:~:text=Deoxyribonucleic%20acid%20(abbreviated%20DNA)%20is,a%20protein%20or%20RNA%20molecule.
ECG: An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a quick, non-invasive, and painless test that records the heart's electrical activity using electrodes on the skin. It checks heart rhythm, identifies arrhythmias, and detects damage from heart attacks or poor blood flow. Common types include resting, exercise, and 24-hour Holter monitors.
EEG: Electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test that measures electrical activity in the brain. In Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) is a critical diagnostic and monitoring tool, as epilepsy affects most patients. Regular, prophylactic EEG surveillance in the first year of life is highly effective at detecting subclinical epileptiform activity (often weeks/months before seizures), allowing for early intervention to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/eeg/about/pac-20393875
Gene: A gene is a stretch of DNA containing a sequence (instruction) with a particular function, such as to make a specific protein. https://www.genomicseducation.hee.nhs.uk/genotes/knowledge-hub/gene/
LAM: Lymphangioleimyomatosis (LAM) is a progressive lung disease occurring in 30–40% of adult women with TSC It is characterized by the proliferation of smooth muscle-like "LAM cells" that cause lung cysts, respiratory failure, and lymphatic abnormalities. While similar to sporadic LAM, TSC-LAM is often associated with renal angiomyolipomas and is managed with mTOR inhibitors like sirolimus. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10672091/
mTOR : The mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) coordinates cell growth and metabolism with environmental inputs including nutrients and growth factors. Mutations in TSC1 or TSC2 genes lead to overactivation of the (mTOR) signaling pathway, causing excessive cell growth and benign tumor (hamartoma) formation. mTOR inhibitors like sirolimus https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3520048/ and everolimus are used to treat TSC-related manifestations by restoring control over this pathway, specifically targeting brain, kidney, and lung tumors. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13023-022-02266-0
List of Abbreviations
ADHD: Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
AEDs: Anti-Epileptic Drugs
AML: Angiomyolipoma
ANP: Advanced Nurse Practitioner
ASD: Autism Spectrum Disorder
BP: Blood Pressure
CAMHS: Child and Adolescent Mental Health Services
CD: Chronic disease
COREQ Guidelines: Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research guidelines
cRHM: Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
CT: Computed tomography
DOH: Department of Health
ECG: Electrocardiogram
ECHO: Echocardiogram
EEG: Electroencephalogram
EEPR: Epilepsy electronic patient record
EHR: Electronic health record
ERDERA: European Rare Diseases Research Alliance
ERN: European Reference Networks (for rare and complex diseases)
ETSC: European Tuberous Sclerosis Complex Association
EU: European Union
EURODRIS: The European Organization for Rare Diseases
FDA: Food and Drug Administration
GP: General Practitioner
HCPs: Healthcare professionals
HRB: The Health Research Board
HRCT: High resolution computerised tomography
HSE: Health Service Executive (ROI)
ID: Intellectual Disability
IDS TILDA: The Intellectual Disability Supplement to the Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing
IQ: Intelligence quotient
IRDiRC: International Rare Disease Research Consortium
IS: Infantile Spasms
ITHACA: Intellectual disability and Congenital Malformations (ERN)
IT: Information Technology
JARDIN: Joint Action on Integration of ERNs into National Healthcare systems
LAM: Lymphangioleiomyomatosis
MDT: Multidisciplinary team
MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging
mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin
mTORi: mTOR inhibitors
NCD: Non-communicable diseases
NGO: Non-governmental organization
NHS: National Health Service (UK)
NORD: National Centre for Rare Diseases
OPH: Ophthalmology
PCN: Primary care network
PKD: Polycystic kidney disease
PPI: Public and Patient Involvement in research
PIL: Patient information leaflet
PNETs: Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
PREMS: Patient Reported Experience Outcomes
PROMS: Patient Reported Outcome Measures
QOL: Quality of life
QPS: Quality and Patient Safety
RAH: Retinal astrocytic hamartoma
RCC: Renal cell carcinoma
RCSI: Royal College of Surgeons Ireland
RD: Rare Disease
RDCTN: Rare Disease Clinical Trial Network
RDI: Rare Diseases International
ROI: Republic of Ireland
SEGA: Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
SEN: Subependymal nodule
SUDEP: Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy
TAND: Tuberous Sclerosis Associated Neuropsychiatric disorders
TANDem: TAND consortium empowering patients through technology
TAND-L: TAND checklist (Lifelong version)
TAND-SQ: TAND checklist (Self-complete version)
TSA: Tuberous Sclerosis Association
TOSCA: TuberOus SClerosis complex registry to increase disease Awareness
TSC: Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
TSC1: Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 1
TSC2: Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2
UK: United Kingdom
UN: United Nations
USA: United States of America
WHO: World health Organization
Yrs.: Years